Understanding Zero Trust Security: Core Principles and Benefits Explained
Understanding Zero Trust Security revolves around several core principles and offers numerous benefits for enhancing cybersecurity. The zero trust model, popularized by Forrester, is based on the mantra to never trust, always verify. This approach aims to reduce the attack surface by enforcing strict access controls and continuous monitoring of systems. At its core, it requires entities to authenticate themselves before gaining access to sensitive data, thereby mitigating the risk of a data breach or ransomware attack.
The zero trust strategy mandates the principle of least privilege, granting the minimum level of access necessary to users, thus preventing lateral movement by malicious actors. Security teams focus on access control within a zero trust environment to protect workloads and data. MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools are integral to this framework, providing continuous oversight of insider threats or breaches.
Adopting a zero-trust approach involves designing a zero-trust architecture that prioritizes secure remote work and improves the user experience by making it easier to adhere to security principles. As organizations move towards this model, they must implement zero trust principles, such as least privilege and robust authentication methods, to ensure comprehensive data protection. The benefits of zero trust security include a reduced risk of a data breach, improved access controls, and a fortified security posture even if an attacker breaches the perimeter.
What Is Zero Trust Security?
Zero trust security is a comprehensive security strategy that challenges the traditional notion of trust within a network. With the zero trust approach, organizations do not inherently trust every user or device, whether they are inside or outside the corporate network. Instead, zero trust requires strict verification for all access requests, granting users the minimum level of access privileges necessary to perform their tasks. This approach is critical in today’s era of digital transformation, where cloud environments and cloud-based applications are pervasive, and traditional security measures are often insufficient. The zero-trust framework leverages technologies like network segmentation and VPNs to ensure that access requests are continuously verified and monitored.
Adopting a zero-trust model involves designing a thorough zero-trust architecture that integrates with existing security policies and incorporates tools that analyze user behaviour. By deploying zero trust, organizations can minimize security breaches by ensuring that access privileges are granted only to trusted individuals, and only for the resources they need. This involves a shift from traditional models to new paradigms, such as using SSO for user authentication, which allows users to access multiple systems with a single password. As companies continue moving to zero trust, they implement processes that ensure users can securely interact with on-premises and cloud services.
Zero trust doesn’t imply a lack of trust in employees, but rather a focus on protecting sensitive data. Zero trust also emphasizes that one part of the network should not automatically trust another, helping to contain potential threats. As organizations engage in designing a zero-trust architecture, they are encouraged to assess and deploy zero-trust strategies that align with their specific needs. In essence, zero trust’s core principle of "never trust, always verify" is integral to modern security strategies, ensuring robust protection across all platforms.

How Does Zero Trust Security Differ From Traditional Security Models?
In recent years, there has been a significant shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity, with many adopting a zero-trust model. Unlike traditional security models that rely heavily on perimeter defences, zero trust security operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." This means that no user or device is inherently trusted, whether inside or outside the network. The traditional models often assumed that threats primarily came from outside the network, focusing on securing the perimeter and granting more trust to internal users. In contrast, zero trust security doesn’t make such assumptions, advocating for a more granular, continuously verified approach to access.
Implementing a zero-trust framework involves understanding the identity and context of the workforce accessing resources. It requires verifying each access request thoroughly before granting it, regardless of the user’s location. This is where Single Sign-On (SSO allows users to access) systems come into play, offering a streamlined way for users to authenticate across various applications while still adhering to core zero trust principles. By requiring continuous verification and employing technologies like multi-factor authentication, the zero trust model provides a robust and adaptable security posture, addressing the evolving threat landscape more effectively than traditional models.
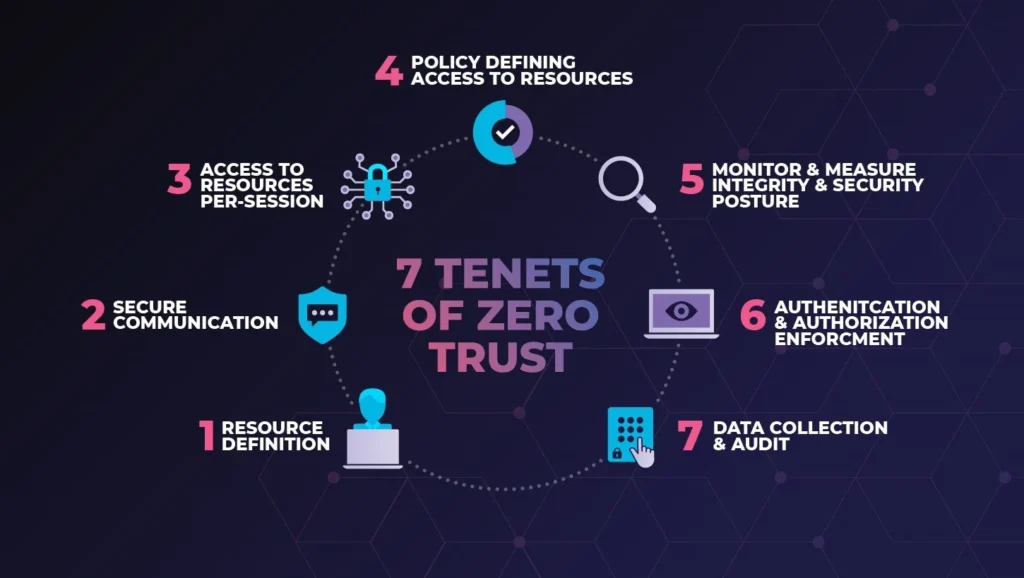
How Does Zero Trust Improve Security Posture?
Adopting a zero trust security model significantly enhances an organization's security posture by fundamentally altering the traditional approach to network access. Unlike conventional models that assume everything within the network perimeter is trustworthy, the zero trust framework operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." This means that every access request is treated as potentially hostile, necessitating thorough verification before granting access. By implementing a zero-trust security strategy, organizations ensure that both internal and external threats are minimized, as no entity is inherently trusted within the network.
Designing a zero trust architecture is crucial for organizations aiming to bolster their defences. This process involves creating a comprehensive strategy that integrates continuous monitoring and validation of user identities and devices. An effective zero trust solution requires organizations to create a zero trust environment that limits access based on strict authentication and authorization policies. This approach not only fortifies the network against malicious actors but also ensures that sensitive data remains protected, regardless of where it resides or who attempts to access it.
Furthermore, the zero-trust security framework aids in maintaining compliance with various regulatory standards by ensuring that access controls are consistently enforced and monitored. This is especially critical in industries that handle sensitive information, such as healthcare and finance. By adopting a zero-trust network access strategy, organizations can effectively safeguard their resources while meeting stringent compliance requirements. Ultimately, it provides a robust defence mechanism that adapts to modern threats, ensuring that security measures evolve in tandem with the threat landscape.
Cost Savings Through Adopting Zero Trust
Adopting a zero-trust architecture can lead to significant cost savings for organizations by reducing security breaches and their associated expenses. The core principle of zero trust is "never trust, always verify," which means that every access request must be authenticated and authorized, regardless of its origin. By implementing such a stringent security model, companies can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches, which are often costly to remediate. This approach not only protects sensitive data but also helps in avoiding regulatory fines and reputational damage.
Moreover, zero trust can streamline IT operations, reducing the need for extensive perimeter-based security measures. Traditional security models often require substantial investments in hardware and software to protect the network boundary. However, with zero trust, organizations focus on securing individual resources and users, potentially lowering the overall costs of security infrastructure. This shift enables businesses to allocate resources more effectively, investing in technologies and processes that directly support their strategic goals.
Additionally, zero trust encourages the adoption of modern, cloud-based solutions, which can offer scalable security features at a lower cost compared to on-premises systems. By leveraging cloud services, organizations can benefit from economies of scale and reduce their total cost of ownership. Overall, the zero trust model not only enhances security but also offers a more cost-effective approach to managing and protecting IT resources.
At Cyber Scope, we’re dedicated helping businesses like yours navigate complex cybersecurity landscape. Contact us today to learn more about our comprehensive solutions tailored to fit your needs. Take proactive steps today by partnering with us—to fortify your digital fortress and ensure continuous growth free from cyber threats. Contact Cyber Scope now to learn how we can enhance your online security posture!
Please contact us for more information




